In 2024, data encryption has become one of the most crucial pillars of cybersecurity. As organizations and individuals manage increasing amounts of sensitive data, the need for robust data encryption practices is more essential than ever. Encryption ensures that unauthorized entities cannot access your data, adding a powerful layer of security against breaches and cyberattacks. This article outlines the best practices for data encryption in 2024, covering the latest encryption techniques, strategies, and methods to protect your information.
What is Data Encryption, and Why is It Important?
Data encryption is the process of converting readable data into an unreadable format using algorithms and encryption keys. Only individuals with the correct key can decrypt this information and read it. As cyber threats continue to evolve, encryption has become an indispensable tool to protect sensitive data, whether stored on local devices, in the cloud, or while being transmitted over the internet.
Companies and individuals alike rely on encryption to protect data from unauthorized access, mitigate security risks, and comply with data protection regulations. Failing to implement encryption increases vulnerability to breaches, and the repercussions of unprotected data can be severe, including data theft, reputational damage, and legal penalties.
Key Best Practices for Data Encryption in 2024
To achieve optimal protection, data encryption practices must be implemented strategically and consistently. Here are the essential practices for robust encryption security in 2024.
1. Use Strong Encryption Algorithms
The encryption algorithm you choose is fundamental to your data security. In 2024, standard algorithms like AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) and RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) are still widely used, with AES-256 and RSA-4096 offering some of the highest levels of security. It’s essential to use these strong, reliable algorithms to reduce vulnerabilities to brute-force attacks.
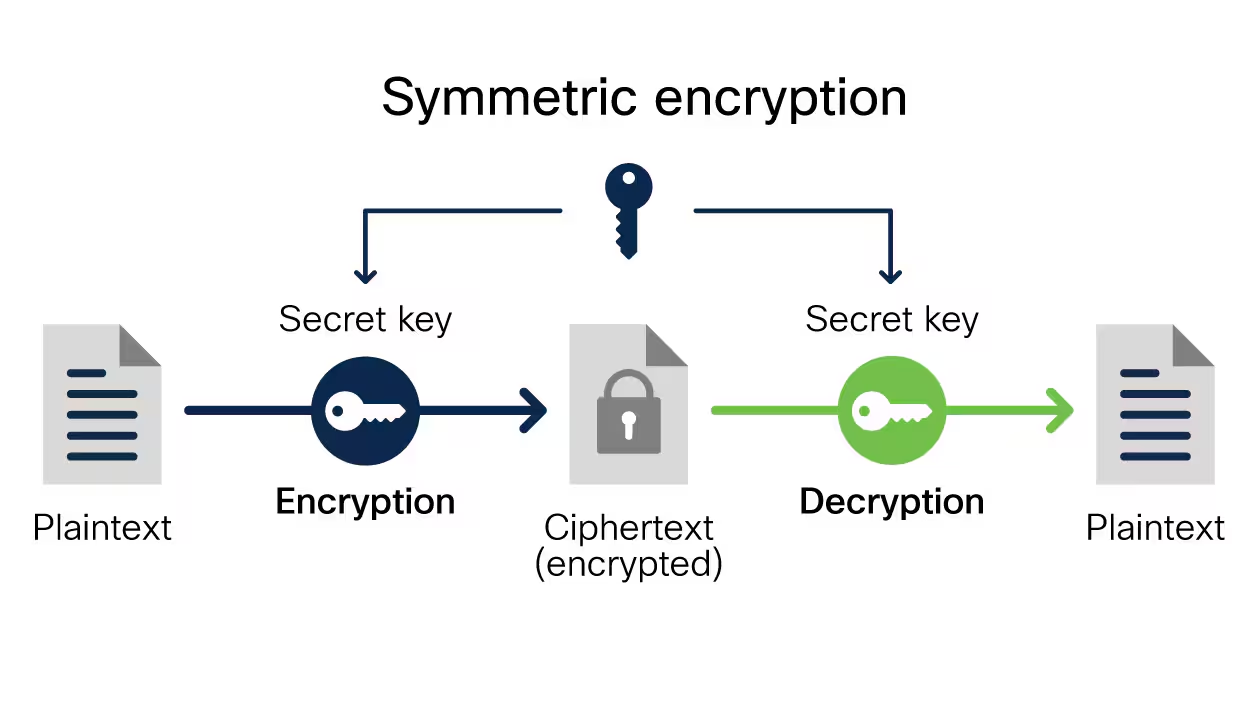
2. Adopt End-to-End Encryption
End-to-end encryption (E2EE) ensures that data is encrypted on the sender’s side and only decrypted by the recipient. This practice is particularly important for securing communications, such as emails or messaging, where sensitive information might be transmitted. In 2024, E2EE is a crucial feature to look for in messaging apps and communication platforms, as it prevents intermediaries from accessing the contents of communications.
3. Encrypt Data at Rest and Data in Transit
Data exists in two primary states: at rest and in transit. Each state presents unique security challenges, requiring different encryption strategies:
Data at Rest: This refers to data stored on a device or server. To protect this data, use disk-level encryption or database encryption. Many cloud providers offer native encryption options for data stored on their servers.
Data in Transit: This includes data being transferred between locations, such as between a user’s device and a server. Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocols are widely used for encrypting data in transit.
4. Implement Encryption Key Management Best Practices
Effective encryption relies on encryption key management. Poor key management practices can lead to unauthorized access, rendering encryption useless. Here are some key management strategies to consider:
- Regularly Rotate Keys: Regular key rotation limits the exposure of encryption keys to potential attackers.
- Use Key Vaults: Secure key vaults like AWS Key Management Service (KMS) or Microsoft Azure Key Vault provide safe storage and management for encryption keys.
- Limit Access: Only allow authorized personnel to access encryption keys. Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) for added security.
5. Encrypt Backups and Archived Data
Many organizations overlook the need to encrypt backup and archived data, which may contain sensitive information. This data can be an easy target for attackers if not properly encrypted. Ensure that all backups, whether on physical drives, cloud storage, or tape storage, are encrypted using strong algorithms.
6. Embrace Quantum-Resistant Encryption Algorithms
The emergence of quantum computing introduces potential vulnerabilities in traditional encryption methods. Quantum-resistant encryption algorithms, also known as post-quantum cryptography, are being developed to withstand attacks from quantum computers. Organizations should start preparing for the future by keeping an eye on post-quantum cryptographic developments and adopting these algorithms as they become available.
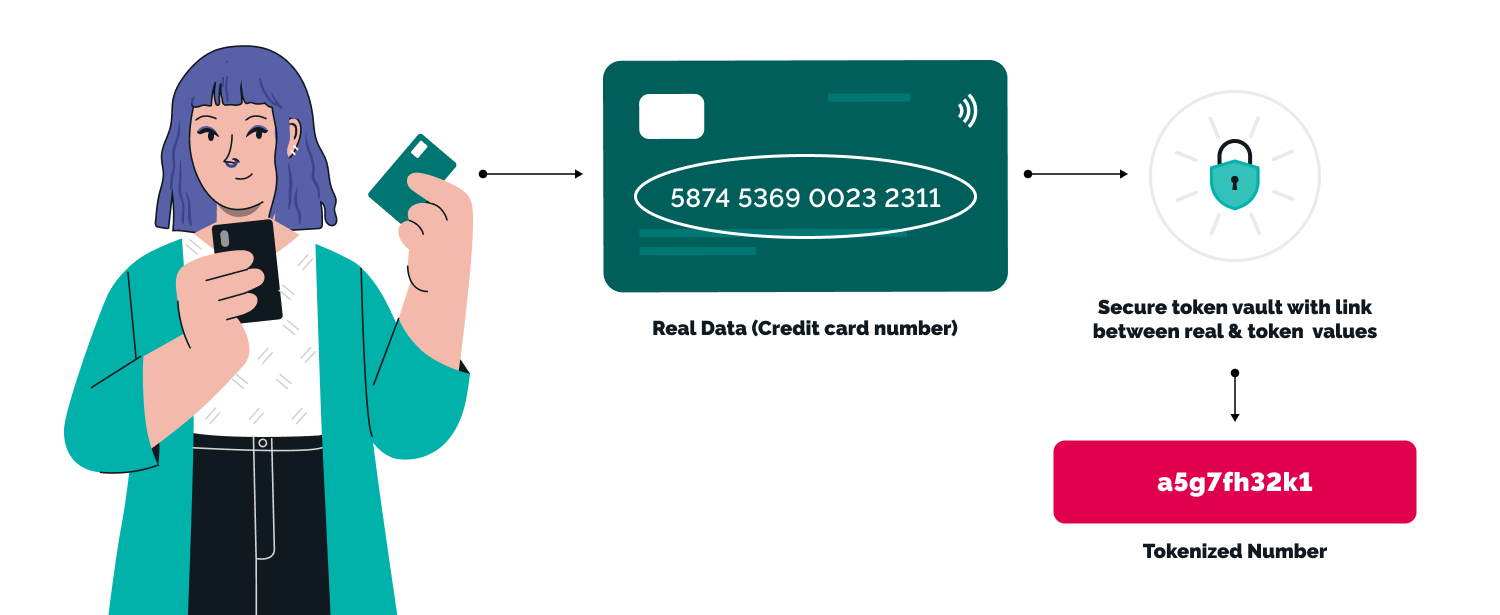
7. Use Tokenization for Sensitive Data
Tokenization replaces sensitive data with unique symbols, or “tokens,” that retain no exploitable value if intercepted. Unlike encryption, which can be decrypted, tokens have no direct relation to the original data, adding an extra layer of security. Tokenization is particularly useful for protecting payment information and personal identification numbers (PINs) in applications like e-commerce and banking.
8. Conduct Regular Encryption Audits
Encryption standards and best practices evolve over time. To maintain strong data security, perform regular encryption audits. These audits should review encryption policies, identify potential weaknesses, ensure compliance with industry standards, and confirm that all data (at rest, in transit, and in use) is properly encrypted.
Why Compliance Matters in Data Encryption
Compliance with data protection regulations is a significant driver for robust encryption practices. Laws such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) in the EU, CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) in California, and HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) in the U.S. mandate data protection for certain types of personal and healthcare data. Non-compliance can result in steep fines and damage to reputation.
Challenges in Data Encryption
Data encryption presents several challenges, especially as data volume and sophistication of cyber threats grow. Below are some common challenges organizations face when implementing encryption:
Performance Impact: Encryption can slow down data retrieval and processing times. Choosing efficient algorithms and high-performance storage solutions can help mitigate this.
Complexity of Key Management: Handling and rotating encryption keys, especially in large organizations, requires specialized knowledge and tools.
Evolving Threats: As encryption technology advances, so do the techniques used by cybercriminals. Constant vigilance and regular updates to encryption protocols are essential to counter new threats.
Cost of Compliance: Meeting regulatory standards requires both time and financial investment. However, the cost of non-compliance or data breach is often far greater.
The Future of Data Encryption in 2024 and Beyond
Looking forward, AI-driven encryption, blockchain-based encryption, and post-quantum encryption technologies are gaining momentum as the future of data security. AI and machine learning are being incorporated to detect vulnerabilities in real-time and provide insights on improving encryption strategies. Quantum computing’s potential to break current encryption methods is also pushing the development of quantum-resistant algorithms.
AI in Data Encryption
AI can analyze vast amounts of data quickly, providing real-time insights into potential security threats and weaknesses in encryption methods. With predictive capabilities, AI tools can proactively adapt encryption protocols to counter emerging threats, making it a valuable asset in data security strategies.
Blockchain for Enhanced Security
Blockchain, with its decentralized structure, adds another layer of security for data. When integrated with encryption, blockchain provides a reliable and transparent ledger system that can help verify data integrity, making it particularly beneficial for industries like finance and supply chain.
Conclusion
In 2024, data encryption remains a cornerstone of cybersecurity, protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access. By adhering to best practices—such as selecting strong encryption algorithms, implementing end-to-end encryption, managing encryption keys effectively, and preparing for quantum-resistant encryption—individuals and organizations can greatly enhance their data security posture. With the rapid advancement in technology, adopting a proactive approach to encryption will be essential to counter evolving cyber threats and safeguard critical data.
Maintaining robust encryption practices is not only a technological imperative but also a critical aspect of responsible data management and regulatory compliance. By focusing on these best practices, organizations can build a resilient defense against breaches and unauthorized data access in an increasingly interconnected digital world.

