The Antimalware Service Executable (ASE) is a critical component of Windows Defender, Microsoft’s built-in antivirus software. While it plays an essential role in maintaining system security, many users have questions about its functions, impact on system performance, and ways to optimize its usage. This article delves into the workings of the Antimalware Service Executable, its importance, and how to handle common issues related to it.
What is Antimalware Service Executable?
The Antimalware Service Executable process (displayed as MsMpEng.exe in the Task Manager) is a part of Microsoft Defender Antivirus. This program is designed to protect Windows systems from malware, spyware, viruses, and other threats. As a core feature of Windows 10 and 11, it runs in the background to ensure real-time protection against security threats.
Key Functions of Antimalware Service Executable
Real-Time Protection: The process continuously monitors system activity for malicious behavior, ensuring that files, programs, and processes are safe.
Threat Scanning: It scans downloaded files, running applications, and system files for potential malware or viruses.
Automatic Updates: The executable regularly updates threat definitions to keep the system protected against emerging threats.
Background Scanning: Periodically scans the system when the computer is idle to detect threats proactively.
Why Does Antimalware Service Executable Use High CPU?
One of the most common complaints about ASE is its high CPU, disk, or memory usage. This behavior typically occurs when:
- Real-Time Scanning: The process is actively scanning files or running programs.
- Full System Scans: Scheduled scans are in progress, particularly if the system has many files.
- Definition Updates: Downloading or applying the latest security updates.
- Conflict with Third-Party Software: Running multiple antivirus programs can cause resource contention.
Is High Resource Usage Normal?
Occasional spikes in CPU or memory usage are normal during scans or updates. However, prolonged or excessive resource consumption may indicate an issue.
How to Resolve High CPU Usage by Antimalware Service Executable
If ASE is consuming excessive resources, consider the following solutions:
1. Schedule Scans for Idle Hours
Windows Defender allows users to schedule scans during periods when the computer is not in use. To adjust the scan schedule:
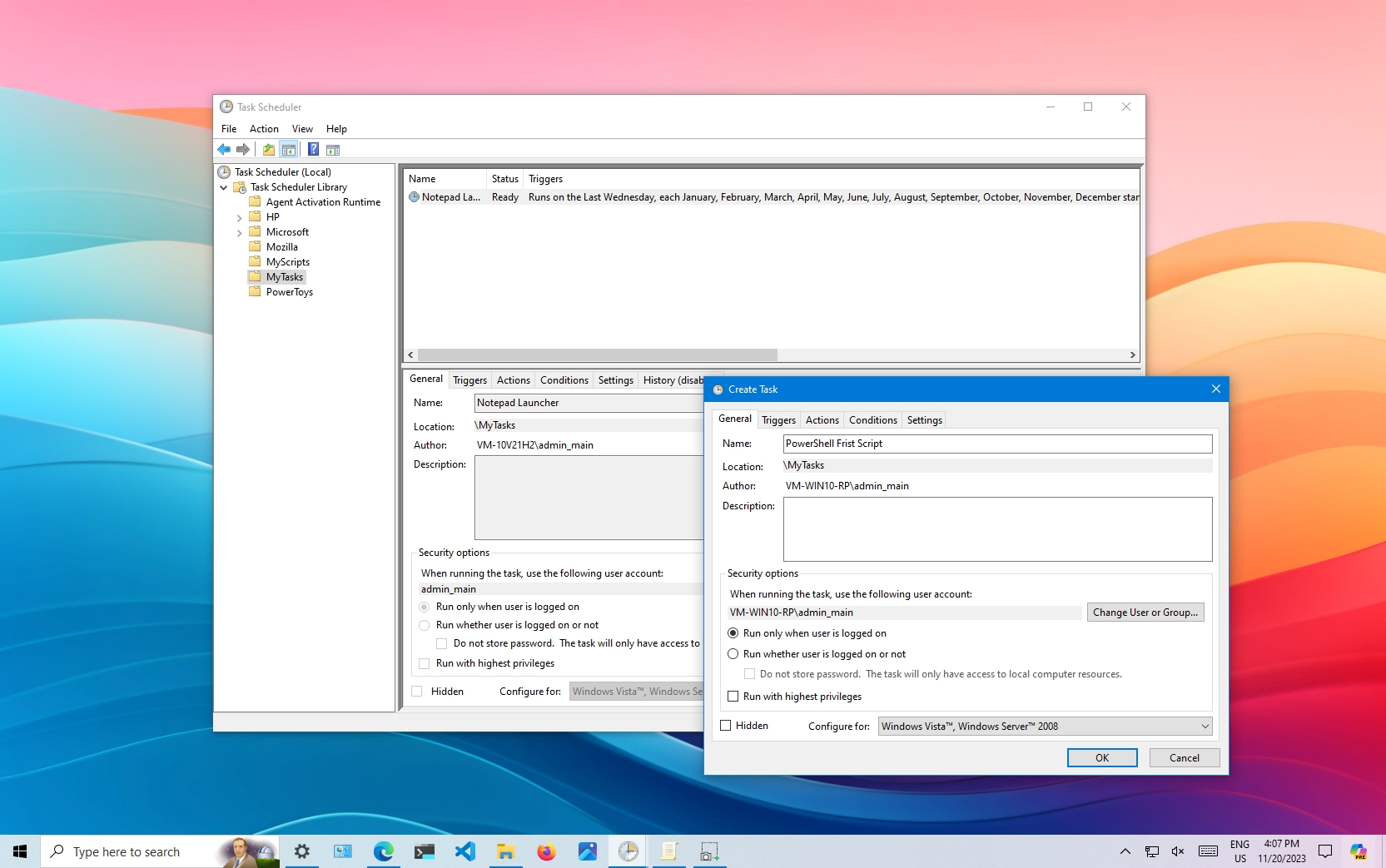
- Open the Task Scheduler (
taskschd.msc). - Navigate to:
Task Scheduler Library > Microsoft > Windows > Windows Defender. - Adjust the Windows Defender Scheduled Scan to run during idle times.
2. Exclude the Antimalware Service Executable Process
Excluding the process from real-time scanning can sometimes reduce resource usage. However, this should be done cautiously as it may expose the system to risks.
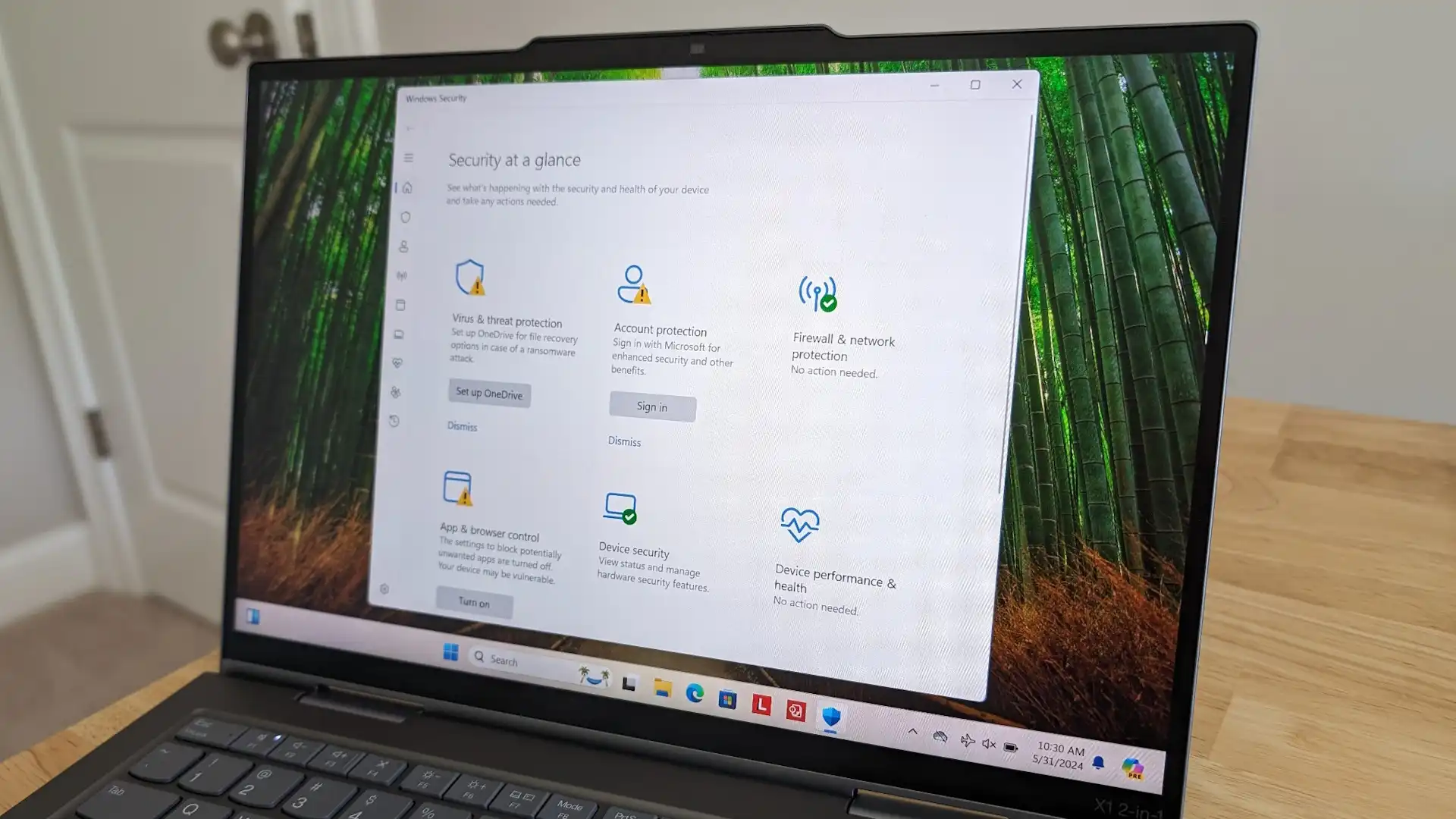
- Open Windows Security.
- Go to Virus & threat protection > Manage settings.
- Scroll to Exclusions > Add or remove exclusions.
- Add the
MsMpEng.exeprocess to the exclusion list.
3. Disable Scheduled Scans
If you have another antivirus program installed, consider disabling Windows Defender scheduled scans to prevent conflicts. Here’s how:
- Open Windows Security.
- Navigate to Virus & threat protection > Manage settings.
- Turn off Real-time protection (temporary measure).
4. Optimize Windows Defender Settings
Adjusting Defender’s settings can help balance performance and protection. For example:
- Disable Cloud-Delivered Protection if it consumes too many resources.
- Enable Tamper Protection to prevent third-party interference.
5. Use a Third-Party Antivirus (If Necessary)
Switching to a lightweight third-party antivirus solution may reduce resource usage if ASE is persistently problematic. However, ensure the antivirus is reliable and regularly updated.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can I Disable Antimalware Service Executable?
Yes, but it’s not recommended. Disabling ASE exposes your system to malware threats. If you still wish to proceed:
- Open Services (
services.msc). - Locate Windows Defender Antivirus Service.
- Right-click and select Stop.
Alternatively, installing a third-party antivirus program will automatically disable Windows Defender.
2. Is Antimalware Service Executable a Virus?
No, ASE is a legitimate Windows process and a core part of Microsoft Defender. However, malware may disguise itself as MsMpEng.exe. To verify its legitimacy:
- Open Task Manager.
- Right-click on
MsMpEng.exeand select Open file location. - Ensure the file is located in the
C:\Program Files\Windows Defenderdirectory.
3. Does Antimalware Service Executable Run on All Windows Systems?
ASE runs on Windows 8, 10, and 11 systems where Microsoft Defender is active. If another antivirus program is installed, the process is typically disabled.
Tips to Optimize System Performance
To reduce the impact of ASE on system performance without compromising security:
- Regularly clean unnecessary files using tools like Disk Cleanup.
- Ensure your system has sufficient memory and storage.
- Keep Windows updated to ensure compatibility and efficiency.
Final Thoughts
The Antimalware Service Executable is a vital component of Windows Defender, providing robust protection against threats. While it may occasionally consume significant resources, the methods outlined above can help minimize its impact on system performance. For most users, ASE is a reliable and essential tool that ensures your computer stays safe from malware.
Remember, the best way to maintain security is to combine good digital hygiene—like avoiding suspicious downloads and websites—with robust antivirus software like Microsoft Defender.

